Fibroblast growth factor-2 content—
Sterile PBS solution—
Prepare a sterile solution that contains 8065.0 mg and 200.0 mg of sodium chloride and potassium chloride, respectively, per L of 0.01 M sodium phosphate buffer, pH 7.4.
Test solution—
Obtain a 1-cm
2 sample of Small Intestinal Submucosa Wound Matrix, weigh, and submerge in 400 µL of
Sterile PBS solution. Pulverize the tissue for 90 seconds using a tissue grinder, intermittently checking to be sure the tissue remains immersed in the
Sterile PBS solution and becomes homogenized. Centrifuge at 12,000 ×
g for 5 minutes at 4

. Use immediately upon preparation.
[NOTE—The
Test solution may be stored for short periods at 4

or on ice.
]
Procedure—
Examine duplicate aliquots of the Test solution by a suitably sensitive ELISA method:1 the analysis is considered valid if the ELISA kit generates a linear standard curve with the square of the correlation coefficient (r2) not less than 0.95, and if the duplicate aliquots of the Test solution yield results that are within 20% of each other. The average content of fibroblast growth factor-2 is not less than 10,000 pg per g of Small Intestinal Submucosa Wound Matrix.
Glycosaminoglycan content—
1,9-Dimethylmethylene blue solution—
Mix 95 mL of 0.1 M hydrochloric acid in 500 mL of water. Add 16 mg of 1,9-dimethylmethylene blue, 3.04 g of aminoacetic acid, and 2.37 g of sodium chloride. Dilute with water to 1 L, and adjust to a pH of 3.0 using sterile solutions of either 1.0 M sodium hydroxide or 1.0 M hydrochloric acid. Store in low-actinic glassware.
Sterile PBS solution—
Prepare as directed under Fibroblast growth factor-2 content.
Proteinase K solution—
Prepare a solution of Tritirachium album proteinase K in water having an activity of 600 units per mL.
Stock heparin standard solution—
Prepare a solution containing 1 mg of heparin per mL of water.
Heparin standard curve solutions—
Using the Stock heparin standard solution, prepare three solutions containing 20 µg per mL, 50 µg per mL, and 100 µg per mL of heparin, respectively.
Blank solution—
Use water.
Test solution—
Prepare test samples in duplicate. Accurately weigh about 25 mg of Small Intestinal Submucosa Wound Matrix and cut into small pieces (roughly 2 mm × 2 mm). Transfer to a 1.5-mL microcentrifuge tube, and add 180 µL of
Sterile PBS solution and 20 µL of
Proteinase K solution. Mix, and incubate the sample at 56

for 15 minutes; during the incubation mix intermittently on a vortex mixer. Cool the sample to room temperature. Dilute with water to obtain a concentration of 12.5 mg of digested Small Intestinal Submucosa Wound Matrix per mL.
Collagen control solution—
Accurately weigh about 25 mg of a bovine collagen, type I, that contains less than 1 µg of glycosaminoglycan per mg. Transfer to a 1.5-mL microcentrifuge tube, and add 180 µL of
Sterile PBS solution and 20 µL of
Proteinase K solution. Mix, and incubate the sample at 56

for 15 minutes; during the incubation mix intermittently on a vortex mixer. Cool the sample to room temperature. Dilute with water to obtain a concentration of 12.5 mg of digested bovine collagen per mL.
Procedure (see Spectrophotometry and Light-Scattering  851
851 )—
)—
To triplicate 100-µL aliquots each of
Heparin standard curve solutions, Blank solution, Test solution, and
Collagen control solution, add 2.5 mL of
1,9-Dimethylmethylene blue solution. Mix on a vortex mixer for 1 second and immediately read the absorbance at 525 nm. Generate a standard curve of absorbance versus concentration using the averages of each
Heparin standard curve solution, correcting for the blank, and calculate the regression line and regression coefficient. The concentration of glycosaminoglycan in the
Test solution and the
Collagen control solution is determined directly from the regression line. If the absorbance of the
Test solution is greater than the highest
Heparin standard curve solution, then dilute the
Test solution appropriately, and repeat the
Procedure beginning with “To triplicate 100-µL aliquots.” The test is considered valid if the regression curve has a square of the correlation coefficient (
r2) not less than 0.95; the triplicate aliquots of the
Test solution and
Collagen control solution yield results that are within 20% of each other, respectively; and the average glycosaminoglycan content of the
Test solution is statistically greater than the
Collagen control solution using one-tailed, unequal variances,
t-test at
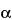
= 0.05. The average glycosaminoglycan content of the
Test solution is not less than 2 µg per mg.
Metabolic activity assessment—
Dulbecco's modified Eagle's tissue culture medium—
Prepare a solution that contains the components included in the following
Table 1:
Table 1
| Component |
Content
(mg per L) |
| Calcium nitrate, tetrahydrate |
100.0 |
| Ferric nitrate, nonahydrate |
0.10 |
| Potassium chloride |
400.0 |
| Magnesium sulfate, anhydrous |
48.840 |
| Sodium chloride |
6,000.0 |
| Sodium bicarbonate |
1,500.0 |
| Sodium phosphate, dibasic (anhydrous) |
800.0 |
| Glucose |
4,500.0 |
| Glutathione (reduced) |
1.0 |
| Phenol red |
5.0 |
| Sodium pyruvate |
110.0 |
| L-Arginine (free base) |
200.0 |
| L-Asparagine, monohydrate |
56.620 |
| L-Aspartic Acid |
20.0 |
| L-Cystine dihydrochloride |
65.20 |
| Aminoacetic acid |
10.0 |
| L-Histidine (free base) |
15.0 |
| Hydroxy-L-proline |
20.0 |
| L-Isoleucine |
50.0 |
| L-Leucine |
50.0 |
| L-Lysine hydrochloride |
40.0 |
| L-Methionine |
15.0 |
| L-Phenylalanine |
15.0 |
| L-Proline |
20.0 |
| L-Serine |
30.0 |
| L-Threonine |
20.0 |
| L-Tryptophan |
5.0 |
| L-Tyrosine, disodium, dihydrate |
28.830 |
| L-Valine |
20.0 |
| D-Biotin |
0.20 |
| D-Calcium pantothenate |
2.50 |
| Choline chloride |
3.0 |
| Folic acid |
1.0 |
| Inositol |
35.0 |
| Nicotinamide |
1.0 |
| p-Aminobenzoic acid |
1.0 |
| Pyridoxine hydrochloride |
1.0 |
| Riboflavin |
0.20 |
| Thiamine hydrochloride |
1.0 |
| Cyanocobalamine |
0.0050 |
MTT reagent—
Use a suitable solution of 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2yl)-2,5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide.2
Detergent reagent—
Use a suitable sodium dodecyl sulfate detergent solution.3
Procedure—
Remove three 12-mm diameter circular sections of Small Intestinal Submucosa Wound Matrix, using the appropriate size biopsy punch. Immerse each section into individual wells of a 12-well cell culture plate (dimension of each well is about 22 to 23 mm in diameter and about 17 to 18 mm in depth), each containing 1 mL of
Dulbecco's modified Eagle's tissue culture medium. Prepare a positive control by harvesting a full-thickness section of porcine jejunum immediately following slaughter. Rinse the section of jejunum in 37

isotonic sodium chloride solution for 5 minutes to remove intestinal debris. Using scissors, split open the section of jejunum to form a sheet. Remove three 12-mm diameter circular sections of jejunum, using the appropriate size biopsy punch. Immerse each section into individual wells of a 12-well cell culture plate, each well containing 1 mL of
Dulbecco's modified Eagle's tissue culture medium. Treat these positive control wells in the same manner as the test wells. Prepare a blank solution using 1 mL of
Dulbecco's modified Eagle's tissue culture medium. Allow sections to hydrate for 5 minutes, add 50 µL of
MTT reagent to each of the sections and the blank, and mix. Incubate for 3 hours at 37

in an atmosphere containing 5% carbon dioxide. Add 100 µL of
Detergent reagent to each well, and mix. Leave the samples at ambient temperature in the dark for 2 hours. Measure the absorbance of the resulting solution at 570 nm, adjusting for the blank. For the test to be valid, the average absorbance in the positive control wells is greater than 0.100. The average absorbance reading for the Small Intestinal Submucosa Wound Matrix wells is less than 0.100.
Bioactivity—
[NOTE—Aseptic cell culture techniques should be employed throughout the performance of this test.
]
Modified RPMI-1640 culture medium—
Prepare a sterile solution that contains the components included in the following
Table 2:
Table 2
| Component |
Content
(mg per L) |
| Calcium chloride |
264.9 |
| Ferric nitrate, nonahydrate |
0.10 |
| Potassium chloride |
400.0 |
| Magnesium sulfate, heptahydrate |
200.0 |
| Sodium chloride |
6,400.0 |
| Sodium bicarbonate |
3,700.0 |
Sodium phosphate, monobasic,
monohydrate |
125.0 |
| Glucose |
4,500.0 |
| Phenol red |
15.0 |
| Sodium pyruvate |
110.0 |
| L-Arginine hydrochloride |
84.0 |
| L-Cystine |
48.0 |
| Aminoacetic acid |
30.0 |
L-Histidine hydrochloride,
monohydrate |
42.0 |
| L-Isoleucine |
104.8 |
| L-Leucine |
104.8 |
| L-Lysine hydrochloride |
146.2 |
| L-Methionine |
30.0 |
| L-Phenylalanine |
66.0 |
| L-Serine |
42.0 |
| L-Threonine |
95.2 |
| L-Tryptophan |
16.0 |
| L-Tyrosine |
72.0 |
| L-Valine |
93.6 |
| L-Calcium pantothenate |
4.0 |
| Choline chloride |
4.0 |
| Folic acid |
4.0 |
| Inositol |
7.0 |
| Nicotinamide |
4.0 |
| Pyridoxine hydrochloride |
4.0 |
| Riboflavin |
0.40 |
| Thiamine hydrochloride |
4.0 |
| Sodium 1-heptanesulfonic acid |
2383.0 |
Penicillin–streptomycin solution—
Prepare a suitable buffered solution containing 10,000 USP Penicillin Units of penicillin per mL and 10 mg of streptomycin per mL.4
PC12 cell line culture medium—
Mix 420 mL of Modified RPMI-1640 culture medium, 50 mL of horse serum,5 25 mL of fetal bovine serum,6 and 5 mL of Penicillin–streptomycin solution. Sterilize by passing through a 0.22-µm filter.
Sterile PBS solution—
Prepare as directed under Fibroblast growth factor-2 content.
Rat tail collagen solution—
Prepare a suspension containing 0.2 mg of rat tail collagen, type I, in sterile water.
Cell culture apparatus—
Prepare by adding a sufficient volume of
Rat tail collagen solution to completely cover the bottom of each well of a 12-well cell culture plate (dimension of each well is about 22 to 23 mm in diameter and about 17 to 18 mm in depth). Incubate under sterile conditions for 2 hours at 37

or overnight at room temperature. Remove the
Rat tail collagen solution by aspiration. Rinse with
Sterile PBS solution that has been preheated to 37

.
PC12 cells—
Use cultured rat pheochromocytoma cells (ATCC CRL-1721).
Cultivation of PC12 cells—
Starting from a frozen culture, prewarm
PC12 cell line culture medium to 37

. Add 15 mL of prewarmed
PC12 cell line culture medium to a T-75 culture flask. Place a single vial containing the frozen
PC12 cells in a 37

water bath with gentle agitation until they start to thaw (about 1 minute). Complete the thawing procedure by slowly rotating the vial between the hands. Rinse the outside of the vial with 70 percent alcohol. Transfer the contents of the vial to the T-75 flask, and mix. Incubate the cells overnight at 37

in a 5% carbon dioxide atmosphere. Transfer the contents of the T-75 culture flask to a sterile centrifuge tube, centrifuge at 200 ×
g for 5 minutes at 37

, and discard the supernatant. Resuspend the cells in 15 mL of
PC12 cell line culture medium, and transfer the contents back into the T-75 culture flask. Incubate the cells at 37

in a 5% carbon dioxide atmosphere for 3 days.
Cell feeding—
At the end of 3 days, the cells will need to be fed for optimal growth. To feed the cells, remove a flask of cells from the incubator, tightening the cap in the process. Examine the T-75 flask under the microscope and check for microbial contamination and confluency. If there is microbial contamination, then discard the flask. If the cells appear confluent, follow the instructions below for perpetuating the PC12 cell line (see
Culture perpetuation). Otherwise, harvest the cells from the flask by pipeting the contents of the flask across the bottom of the flask several times. Transfer the cell suspension to a sterile 50-mL centrifuge tube. Centrifuge the cells at 200 ×
g for 5 minutes at 37

, and discard the supernatant. Resuspend the cells in 13 mL of
PC12 cell line culture medium, prewarmed to 37

. Transfer the cell suspension back to the T-75 flask, and mix. Loosen the cap of the flask, and return to the incubator; incubate the cells at 37

in a 5% carbon dioxide atmosphere for another 3 to 7 days.
Culture perpetuation—
To perpetuate a line of
PC12 cells for culture, examine under the microscope a T-75 flask containing cells and check for microbial contamination and confluency. If there is microbial contamination, discard the flask and use another. If the cells do not appear confluent, then follow the instructions above for feeding the PC12 cell line (see
Cell feeding), beginning with “Otherwise, harvest the cells from the flask by pipeting the contents of the flask across the bottom of the flask several times.” If the cells are confluent and there is no contamination, harvest the cells from the flask by pipeting the contents of the flask across the bottom of the flask several times to loosen up the cells from their attachment to the bottom of the flask and to break up cell clusters. Check under the microscope prior to proceeding to ensure that most of the cells have detached from the plastic. Transfer the cell suspension to a sterile 50-mL centrifuge tube, and centrifuge the cells at 200 ×
g for 5 minutes at 37

. Discard the supernatant and resuspend the cells with 10 mL of
PC12 cell line culture medium, prewarmed to 37

. Dispense an equal amount of the cell suspension into each of three to five T-75 flasks, each flask containing 10 mL of
PC12 cell line culture medium, prewarmed to 37

, and mix. Return the passed cells to the incubator, being sure to loosen the cap of the flasks. Incubate the cells at 37

in a 5% carbon dioxide atmosphere. Feed the cells after 3 days as directed above, beginning with “To feed the cells, remove a flask of cells from the incubator, tightening the cap in the process.”
[NOTE—To perform the test for
Bioactivity, cells that have undergone more than 15 passages after obtaining them from ATCC should not be used.
]
Positive control solution—
Prepare a solution containing about 10 ng of fibroblast growth factor-2 per mL of PC12 cell line culture medium.
Negative control solution—
Use PC12 cell line culture medium.
Test solution—
Immerse 70 cm
2 of Small Intestinal Submucosa Wound Matrix in sterile water for 5 minutes. Remove the Small Intestinal Submucosa Wound Matrix, and blot excess water using sterile gauze. Weigh the rehydrated Small Intestinal Submucosa Wound Matrix to the nearest 0.1 g and add
Modified RPMI-1640 culture medium at a ratio of 7.5 mL of
Modified RPMI-1640 culture medium for each 1.0 g of Small Intestinal Submucosa Wound Matrix. Incubate for 24 hours at 37

with constant shaking. Remove the Small Intestinal Submucosa Wound Matrix, and pass the solution through a 0.22-µm filter. Add sufficient quantities of sterile horse serum and sterile fetal bovine serum to concentrations of 10% and 5%, respectively, and add a sufficient quantity of
Penicillin–streptomycin solution such that there are 100 USP Penicillin Units and 0.1 mg of streptomycin per mL. Adjust the pH of the
Test solution to 7.4, using a sterile solution of either 1.0 M sodium hydroxide or 1.0 M hydrochloric acid.
Procedure—
Harvest a flask of confluent
PC12 cells by centrifuging at 200 ×
g for 5 minutes. Remove the supernatant by aspiration, and resuspend the pellet to obtain a concentration of about 1 × 10
6 cells per mL of
PC12 cell line culture medium. Add to each of three wells of the
Cell culture apparatus 1.0 mL of
Negative control solution. To a second set of three wells add to each 1.0 mL of
Positive control solution, and to a third set of three wells add to each 1.0 mL of
Test solution. Add to each well about 20,000 cells, mix by gentle rocking, and incubate for 48 hours at 37

. For each well, count three random microscopic fields of cells using a microscope with a 10× ocular lens and a 20× objective lens. Each field should have at least 20 cells; avoid large clumps of cells where individual cell bodies cannot be ascertained. Determine the total number of cells in the field and, using USP Cultured Rat Pheochromocytoma Reference Photomicrographs of normal and differentiated rat pheochromocytoma cells for comparison, determine the total number of cells that have formed at least one neurite-like extension at least twice the diameter of a normal, undifferentiated cell body. For each experimental group, record the total number of cells counted and the total number of cells differentiated across all three wells, and calculate the total percentage of cells that have differentiated. For a test to be valid, the following criteria must be met: (1) none of the wells are microbially contaminated; (2) the weighted percentage of differentiated cells across the
Negative control solution wells is less than 5%; (3) the weighted percentage of differentiated cells across the
Positive control solution wells is greater than 6%; and (4) the weighted percentage of differentiated cells across the
Negative control solution wells is statistically less than the weighted percentage of differentiated cells across the
Positive control solution wells, using a one-sided, two-sample test for proportions at
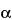
= 0.05. The weighted percentage of differentiated cells incubated in the
Test solution wells is statistically greater than those incubated in the
Negative control solution wells, using a one-sided, two-sample test for proportions at
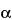
= 0.05.