Procedure—
Transfer about 1.0 g of each
Sample preparation, accurately weighed, into separate 400-mL, tall-form beakers. Add 50 mL of
Phosphate buffer, and adjust the pH, if necessary, to 6.0 ± 0.1. Add 0.2 mL of heat-stable
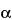
-amylase solution. Cover the beaker with aluminum foil, place in a boiling water bath for 15 minutes at 100

, shaking gently every 5 minutes, and cool to room temperature. Adjust with about 10 mL of 0.275 N sodium hydroxide solution to a pH of 7.5 ± 0.1. Add freshly prepared
Protease solution, cover the beaker with aluminum foil, and incubate for 30 minutes at 60

with continuous agitation. Cool, and add about 10 mL of 0.325 N hydrochloric acid and adjust to a pH of 4.5 ± 0.2. Add 0.3 mL of amyloglucosidase, cover with aluminum foil, and incubate for 20 minutes at 60

with continuous agitation. Heat 280 mL of alcohol to 60

, add to the digest, and allow the precipitate to form at room temperature for 60 minutes. Place 0.5 g of chromatographic siliceous earth in a crucible with fritted disk, dry at 130

to constant weight, and weigh. Wet the chromatographic siliceous earth in the crucible by using a stream of 78% alcohol from a washing bottle, and apply suction to evenly distribute the chromatographic siliceous earth over the fritted disk. Maintain suction, and quantitatively transfer the enzyme digest precipitate to the crucible. Wash the residue successively with three 20-mL portions of 78% alcohol, two 10-mL portions of alcohol, and two 10-mL portions of acetone. In some cases, gums may form during filtration, trapping liquid in residue. If so, break the surface film with a spatula to improve filtration. Dry the crucible containing the residue at 105

in an air oven for 16 hours, cool in a desiccator, and determine the weight of the residue. Determine the percentage of protein in the first
Sample preparation as directed for
Limit of protein. Incinerate the residue from the second
Sample preparation as directed for
Total Ash under
Articles of Botanical Origin  561
561
. Calculate the corrected weight,
W, of the sample residue by the formula:
WU (1
 PU
PU / 100
 AU
AU / 100)
 WB
WB (1
 PB
PB / 100
 AB
AB / 100),
in which
WU and
WB are the average weights of the sample residues and the blank residues, respectively;
PU and
PB are percentages of protein present in the sample and in the blank, respectively; and
AU and
AB are percentages of ash found in the sample and in the blank, respectively. Then calculate the percentage of the total dietary fiber in the portion of Wheat Bran taken by the formula:
100W / WI,
in which
WI is the weight of the
Sample preparation taken. Correct the final percentage of the total dietary fiber for fat and for water: not less than 36.0% is found.