Benzenemethanol, 4-hydroxy-
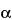
-[1-[(1-methyl-2-phenoxyethyl)amino]ethyl]-, hydrochloride, stereoisomer.
p-Hydroxy-
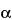
-[1-[(1-methyl-2-phenoxyethyl)amino]ethyl]benzyl alcohol hydrochloride.
(±)-(
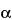 R
R*)-
p-Hydroxy-
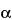
-[(1
S*)-1-[[(1
S*)-1-methyl-2-phenoxyethyl]amino]ethyl]benzyl alcohol hydrochloride



[
579-56-6;
34331-89-0].
Packaging and storage—
Preserve in tight containers.
Identification—
C:
To 1 mL of a solution (1 in 100), obtained by heating as necessary, add 3 mL of a 1 in 15 solution of sodium nitrite in 2 N sulfuric acid. Add ammonium hydroxide dropwise: a yellow precipitate is formed and it dissolves upon the addition of sodium hydroxide solution (1 in 5).
D:
To 1 mL of a solution (1 in 100) add 1 mL of phosphomolybdic acid solution (1 in 100): a pale yellow to white precipitate is formed.
pH  791
791 :
:
between 4.5 and 6.0, in a solution (1 in 100).
Heavy metals, Method II  231
231 :
:
0.002%.
Related compounds—
To 10 mg, accurately weighed in a suitable vial, add 1 mL of N-trimethylsilylimidazole, and heat at 65

for 10 minutes. Add 5 mL of isooctane, wash with one 3-mL portion of water, and allow the layers to separate. Inject a 2-µL portion of the isooctane solution into a gas chromatograph equipped with a 0.3-cm × 2.0-m glass column packed with packing S1A containing 3% liquid phase G2 and a flame-ionization detector. The column temperature is maintained at 215

, and the injection port and detector are maintained at 250

. The carrier gas is nitrogen, flowing at the rate of 25 mL per minute. Adjust the instrument to provide full-scale response for the major component. Inject a second 2-µL portion of the isooctane solution with the attenuator adjusted to an 8-fold increase in sensitivity, and record the chromatogram from 0.5 to 1.5 relative to the retention time of the major peak. Measure the area of all minor peaks, and correct for differences in sensitivity settings. Calculate the percentage of related compounds present taken by the formula:
100A / B,
in which
A is the sum of the corrected area peaks for all minor peaks, and
B is the sum of the corrected area peaks for the major and minor peaks. Not more than 2.0% is found.
Organic volatile impurities, Method V  467
467 :
:
meets the requirements.
Solvent—
Use dimethyl sulfoxide.
Assay—
Transfer about 50 mg of Isoxsuprine Hydrochloride, accurately weighed, to a 1000-mL volumetric flask, add water to volume, and mix. Concomitantly determine the absorbances of this solution and of a Standard solution of
USP Isoxsuprine Hydrochloride RS in the same medium having a known concentration of about 50 µg per mL in 1-cm cells at the wavelengths of maximum absorbance at about 269 and 300 nm, with a suitable spectrophotometer, using water as the blank. Calculate the quantity, in mg, of C
18H
23NO
3·HCl in the Isoxsuprine Hydrochloride taken by the formula:
C(
AU269 AU300
AU300) / (
AS269  AS300
AS300),
in which
C is the concentration, in µg per mL, of
USP Isoxsuprine Hydrochloride RS in the Standard solution; and the parenthetic expressions are the differences in the absorbances of the two solutions at the wavelengths indicated by the subscripts, for the assay solution (
U) and the Standard solution (
S), respectively.