Identification of crystalline materials can be accomplished by comparison of X-ray powder diffraction patterns obtained for known
2 materials with those of the unknown. The intensity ratio (ratio of the peak intensity of a particular
d spacing to the intensity of the strongest maxima in the diffraction pattern) and the
d spacing are used in the comparison. If a reference material (e.g., USP Reference Standard) is available, it is preferable to generate a primary reference pattern on the same equipment used for running the unknown sample, and under the same conditions. For most organic crystals, it is appropriate to record the diffraction pattern to include values for 2
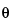
that range from as near zero degrees as possible to 40 degrees. Agreement between sample and reference should be within the calibrated precision of the diffractometer for diffraction angle (2
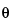
values should typically be reproducible to ±0.10 degrees), while relative intensities between sample and reference may vary considerably. For other types of samples (e.g., inorganic salts), it may be necessary to extend the 2
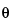
region scanned to well beyond 40 degrees. It is generally sufficient to scan past the ten strongest reflections identified in the Powder Diffraction File.
2