IgG-Coated Red Cells—
Red cells coated with human immunoglobulin (IgG). The reagent must be obtained from manufacturers or suppliers licensed by the Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research, Food and Drug Administration. The use of reagents from an unlicensed manufacturer or supplier may invalidate the results.
[NOTE—There are many manufacturers and suppliers of these reagents that are licensed by the Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research, Food and Drug Administration. Some examples of licensed manufacturers or suppliers are the following: Gamma Biologics, Houston, TX; and Ortho Diagnostics, Raritan, NJ.]
Imidazole,

C
3H
4N
2—
68.08—White to light yellow crystals. Freely soluble in water. Use ACS reagent grade.
Iminostilbene,

C
14H
11N—
193.24—Yellow-orange powder. Sparingly soluble in ethyl acetate.
Indene,

C
9H
8—
116.16—Colorless liquid.
Assay—
Inject an appropriate specimen into a suitable gas chromatograph (see
Chromatography  621
621
) equipped with a flame-ionization detector, helium being used as the carrier gas. The following conditions have been found suitable: a 0.25-mm × 10-m capillary column coated with a 1-µm layer of methylsilicone; the injection port temperature is maintained at 200

; the detector temperature is maintained at 300

; the column temperature is maintained at 100

and programmed to rise 10

per minute to 250

. The area of the indene peak is not less than 99% of the total peak area.
Indicators
—See separate subsection.
Indigo Carmine
—Use Indigotindisulfonate Sodium.
Indole
(2,
3-Benzopyrrole),

C
8H
7N—
117.14


[
170-72-9]—Use a suitable grade.
Indole-3-carboxylic Acid,

C
9H
7NO
2—
161.2


[
771-50-6]—Use a suitable grade.
Inosine,

C
10H
12N
4O
5—
268.23—White, crystalline powder.
Change to read:
Inositol
(
Hexahydroxycyclohexane),

C
6H
6(OH)
6—
180.16—Fine, white crystals or a white, crystalline powder;

 USP29
USP29 stable in air. Its solutions are neutral to litmus. Optically inactive. One g dissolves in 5.7 mL of water. Slightly soluble in alcohol; insoluble in ether and in chloroform. Store in well-closed containers.
Residue on ignition (Reagent test):
not more than 0.1%.
Iobenguane Sulfate
(
m-Iodobenzylguanidine Hemisulfate Salt),

C
8H
10IN
3·½H
2SO
4—
324.1—White powder. Freely soluble in methanol.
Assay—
When tested by thin-layer chromatography, with the use of plates coated with chromatographic silica gel mixture, a developing system consisting of a mixture of butyl alcohol, water, and acetic acid (60:25:15), and examined under short-wavelength UV light, not more than a single impurity spot of not more than 0.5% is observed.
Iodic Acid,

HIO
3—
175.91—Use ACS reagent grade.
Iodine,

I
2—
253.81—Use ACS reagent grade.
Iodine Monobromide,

IBr—
206.81—Black, gray or blue-purple crystals, crystalline needles, or crystalline chunks.
Assay—
Place about 100 mL of acetic acid in a 150-mL beaker. Separately dissolve 2 g of potassium iodide in a minimum volume of water, add this solution to the acetic acid, and mix. Transfer about 200 mg of Iodine Monobromide, accurately weighed, to the beaker containing the potassium iodide and acetic acid mixture, and stir to dissolve. Titrate immediately with 0.1 N sodium thiosulfate VS, determining the endpoint potentiometrically (see
Titrimetry  541
541
). Perform a blank determination, and make any necessary correction. Each mL of 0.1 N sodium thiosulfate is equivalent to 20.681 mg of IBr. Not less than 97.5% is found.
Iodine Monochloride,

ICl—
162.36—Use ACS reagent grade.
Iodoethane,

C
2H
5I—
155.9 


[
75-03-6]—Use a suitable grade.
p-Iodonitrotetrazolium Violet,
(2-(4-Iodophenyl)-3-(4-nitrophenyl)-5-phenyltetrazolium chloride),

C
19H
13ClIN
5O
2—
505.70—Light yellow powder.
Assay—
When tested by thin-layer chromatography, with the use of plates coated with chromatographic silica gel mixture and a developing system consisting of a mixture of amyl alcohol, formic acid, and water (8:1:1), sprayed with 0.1% sodium thiosulfate solution, and examined under short-wavelength UV light, a single spot is exhibited, with trace impurities.
Ion-Exchange Resin
—An intimate mixture of 4 parts of a strongly acidic cation-exchanger in the hydrogen form (produced by sulfonation of a styrene-divinylbenzene copolymer, representing 8 to 10% divinylbenzene) and 6 parts of a strongly basic anion-exchanger in the hydroxyl form (produced by amination with trimethylamine of a chloromethylated styrene-divinylbenzene copolymer, representing 3 to 5% divinylbenzene).
Iron Wire,

Fe—
At. Wt. 55.847—Use a suitable grade.
Isoamyl Alcohol
—Use Amyl Alcohol.
Isobutyl Acetate,

C
6H
12O
2—
116.16—Clear, colorless liquid. Slightly soluble in water. Miscible with alcohol.
Assay—
Inject an appropriate specimen into a suitable gas chromatograph (see
Chromatography  621
621
) equipped with a flame-ionization detector, helium being used as the carrier gas. The following conditions have been found suitable: a 0.25-mm × 30-m capillary column coated with G2. The injection port temperature is maintained at 130

; the column temperature is maintained at 30

and programmed to rise 10

per minute to 180

and held there for 10 minutes. The detector temperature is maintained at 300

. The area of the main peak is not less than 99% of the total peak area.
Isobutyl Alcohol
(
2-Methyl-1-propanol),

(CH
3)
2CHCH
2OH—
74.12—Use ACS reagent grade.
4-Isobutylacetophenone,

C
12H
16O—
176—Pale yellow liquid. Soluble in chloroform, in glycerols, in alcohols, in ether, and in fatty oils; insoluble in water. Use a suitable grade.
N-Isobutylpiperidone,

C
9H
17NO—
155.24—Use a suitable grade.
Isoflupredone Acetate
(9-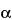 -Fluoroprednisolone Acetate),
-Fluoroprednisolone Acetate),

C
23H
29FO
6—
420.47—Use Isoflupredone Acetate USP.
Isomaltotriose (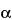 -D-Glucosyl-(1-6)-
-D-Glucosyl-(1-6)-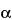 -D-glucosyl-(1-6)-
-D-glucosyl-(1-6)-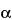 -D-glucose),
-D-glucose),

C
18H
32O
16—
504.4 


[
3371-50-4]—White lyophilized powder. Use a suitable grade.
Isonicotinic Acid,

C
6H
5NO
2—
123.11—Use a suitable grade.
Isonicotinic Acid Hydrazide
—Use Isoniazid.
Isopropyl Acetate,

C
5H
10O
2—
102.13


[
108-21-4]—Use a suitable grade.
Isopropyl Alcohol
(
2-Propanol),

(CH
3)
2CHOH—
60.10—Use ACS reagent grade.
[NOTE—For use in assays and tests involving UV spectrophotometry, use ACS reagent grade Isopropyl Alcohol Suitable for Use in UV Spectrophotometry.]
Isopropyl Alcohol, Dehydrated
—Use Isopropyl Alcohol that previously has been dried by being shaken with a suitable molecular sieve capable of adsorbing water, and filtered.
Isopropyl Iodide
(
2-Iodopropane),

C
3H
7I—
169.99—Colorless liquid, discoloring upon exposure to air and light. Sparingly soluble in water; miscible with alcohol, with benzene, with chloroform, and with ether.
Density:

between 1.696 and 1.704.
Isopropyl Myristate,

C
17H
34O
2—
270.45—Use
Isopropyl Myristate (NF monograph). For use as a solvent in sterility test procedures, Isopropyl Myristate conforms to the following additional specification:
pH of water extract—
Transfer 100 mL to a 250-mL centrifuge bottle, add 10 mL of twice-distilled water, close the bottle with a suitable closure, and shake vigorously for 60 minutes. Centrifuge the mixture at 1800 rpm for 20 minutes, aspirate the upper (isopropyl myristate) layer, and determine the pH of the residual water layer: the pH is not less than 6.5.
Isopropyl Myristate not conforming to the test for pH of water extract may be rendered suitable for use in sterility test procedures as follows:
Using a 20-mm × 20-cm glass column, add activated alumina, and tamp down to a height of 15 cm. Pass 500 mL of the isopropyl myristate through the column, using a slight positive pressure to maintain an even flow, and use the eluate collected directly in the sterility test procedure.
Isopropyl Salicylate,

C
6H
4OHCOOCH(CH
3)
2—
180.20—Colorless liquid.
Assay—
Inject an appropriate specimen into a suitable gas chromatograph (see
Chromatography  621
621
) equipped with a flame-ionization detector, helium being used as the carrier gas. The following conditions have been found suitable: a 2-mm × 1.8-m glass column packed with 7% phase G2 on support S1A; the injection port temperature is maintained at 250

; the detector temperature is maintained at 310

; the column temperature is maintained at 50

and programmed to rise 10

per minute to 250

. The area of the main peak is not less than 97% of the total peak area.
Change to read:
Isopropylamine
(
2-Aminopropane),

C
3H
7NH
2—
59.11—Clear, colorless, flammable liquid.

 USP29
USP29 Miscible with water, with alcohol, and with ether.
Assay—
Transfer about 0.2 g, accurately weighed, to a suitable container, add 50 mL of water, and mix. Titrate with 0.1 N hydrochloric acid VS, using a mixture of
bromocresol green TS and methyl red TS (5:1) as indicator. Each mL of 0.1 N hydrochloric acid is equivalent to 59.11 mg of C
3H
9N. Not less than 98% is found.
Boiling range (Reagent test)—
Not less than 95% distills between 31

and 33

.
Isorhamnetin,

C
16H
12O
7—
316.27


[
418-19-3]—Yellow powder.
Melting point:
greater than 300

.
Isovaleric Acid
 (3-Methylbutanoic Acid, Isovalerianic Acid, Isopropylacetic Acid),
(3-Methylbutanoic Acid, Isovalerianic Acid, Isopropylacetic Acid), C
5H
10O
2—
102.13


[
503-74-2]—Use a suitable grade.