Identification—
A:
Infrared Absorption  197K
197K
—
Test specimen—
Dissolve 10 mg in 5 mL of water, add 0.5 mL of 5 N sodium hydroxide, and extract with 5 mL of methylene chloride. Filter the organic extract through anhydrous sodium sulfate, and evaporate the organic extract to a volume of about 0.5 mL.
B:
The retention time of the major peak in the chromatogram of the Test solution corresponds to that in the chromatogram of the Diluted standard solution, as obtained in the test for Related compounds.
C:
To 0.1 mL of a solution containing the equivalent of about 15 mg of tartaric acid per mL, add 0.1 mL of a 100 g per L solution of potassium bromide, 0.1 mL of a 20 g per L solution of resorcinol, and 3 mL of sulfuric acid. Heat on a hot water bath for 5 to 10 minutes until a dark blue color develops. Allow to cool, and pour the solution into water. The color changes to red (presence of tartrate).
Related compounds—
Phosphate buffer—
Dissolve 6.9 g of monobasic sodium phosphate in 900 mL of water. Adjust with phosphoric acid to a pH of 4.2, dilute with water to 1000 mL, and mix.
Mobile phase—
Dissolve 1.22 g of sodium 1-decanesulfonate in 620 mL of methanol. Add 380 mL of
Phosphate buffer, mix, filter, and degas. Make adjustments if necessary (see
System Suitability under
Chromatography  621
621
).
System suitability solution—
Dissolve accurately weighed quantities of
USP Vinorelbine Tartrate RS and
USP Vinorelbine Related Compound A RS in water, and dilute quantitatively, and stepwise if necessary, with water to obtain a solution having known concentrations of about 1.4 mg per mL and 0.01 mg per mL, respectively. Expose a portion of this solution in a suitable xenon lamp apparatus capable of supplying a dose of 1600 KJ/m
2 between 310 and 800 nm at a power of 500 W/m
2 for about one hour, in order to generate an additional degradation product (3
¢,4
¢,7,8-tetradehydro-3,4
¢-dideoxy-3,6-epoxy-6,7-dihydro-C
¢-norvincaleukoblastine) having a relative retention time of about 0.8.
Standard solution—
Dissolve an accurately weighed quantity of
USP Vinorelbine Tartrate RS in
Mobile phase, and dilute quantitatively, and stepwise if necessary, with
Mobile phase to obtain a solution having a known concentration of about 1.4 mg per mL.
Diluted standard solution—
Transfer 1.0 mL of the Standard solution to a 50-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with Mobile phase to volume. Pipet 1.0 mL of this solution into a 100-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with Mobile phase to volume.
Test solution—
Transfer about 35 mg of Vinorelbine Tartrate, accurately weighed, to a 25-mL volumetric flask, dissolve in and dilute with Mobile phase to volume, and mix.
Chromatographic system (see Chromatography  621
621 )—
)—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a 267-nm detector and a 3.9-mm × 15-cm column that contains 5-µm packing L1. The column temperature is maintained at 40

. The flow rate is about 1.0 mL per minute. Chromatograph the
System suitability solution, and record the peak responses as directed for
Procedure: the retention time for vinorelbine is about 13.5 minutes; and the relative retention times are about 0.8 for the photodegradation product, 1.0 for vinorelbine, and 1.2 for vinorelbine related compound A. The relative retention,
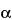
, between vinorelbine tartrate and vinorelbine related compound A is not less than 1.1.
Procedure—
Separately inject equal volumes (about 20 µL) of the
Test solution and the
Diluted standard solution into the chromatograph, record the chromatograms, and measure the areas for the major peaks. Record the chromatograms for three times the retention time of the vinorelbine peak. Disregard any peaks with an area less than or equal to one-half of the area of the peak obtained for vinorelbine in the
Diluted standard solution. Calculate the percentage of each impurity in the portion of Vinorelbine Tartrate taken by the formula:
100(ri / rs),
in which
ri is the peak response for each impurity obtained from the
Test solution; and
rs is the sum of the responses of all the peaks: not more than 0.3% of the photodegradation product is found; not more than 0.2% of any individual impurity or coeluted impurities comprising an individual peak is found; and not more than 0.7% of total impurities, excluding the photodegradation product, is found.
Assay—
Dissolve about 350 mg of Vinorelbine Tartrate, accurately weighed, in 40.0 mL of glacial acetic acid. Titrate with 0.1 N perchloric acid VS, determining the endpoint potentiometrically, using suitable electrodes. Perform a blank determination, and make any necessary correction (see
Titrimetry  541
541
). Each mL of 0.1 N perchloric acid is equivalent to 53.96 mg of C
45H
54N
4O
8·2C
4H
6O
6.