(C
17H
23NO
3)
2·H
2SO
4·2H
2O





712.85
Benzeneacetic acid,
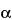
-(hydroxymethyl)-, 8-methyl-8-azabicyclo[3.2.1]oct-3-yl ester, [3(
S)-
endo]-, sulfate (2:1), dihydrate.
1
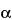 H
H,5
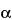 H
H-Tropan-3
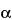
-ol (

)-tropate (ester) sulfate (2:1) (salt) dihydrate



[
6835-16-1].
Anhydrous
676.83



[
620-61-1].
Packaging and storage—
Preserve in tight, light-resistant containers.
Identification—
B:
To about 1 mL of a solution (1 in 20) add gold chloride TS, dropwise with shaking, until a definite precipitate separates. Add a small amount of 3 N hydrochloric acid, dissolve the precipitate with the aid of heat, and allow the solution to cool: lustrous golden yellow scales are formed (distinction from atropine and scopolamine).
C:
A solution (1 in 20) responds to the tests for
Sulfate  191
191
.
Specific rotation  781S
781S :
:
not less than

24

.
Test solution:
50 mg per mL, in water.
Loss on drying  731
731 —
—
Dry it in vacuum at 105

for 16 hours: it loses between 2.0% and 5.5% of its weight.
Other alkaloids—
Dissolve 250 mg in 1 mL of 0.1 N hydrochloric acid, and dilute with water to 15 mL. To 5 mL of the solution add a few drops of
platinic chloride TS: no precipitate is formed. To another 5-mL portion add 2 mL of 6 N ammonium hydroxide: the mixture may develop a slight opalescence, but no turbidity or precipitate is formed immediately.
Organic volatile impurities, Method I  467
467 :
:
meets the requirements.
Assay—
Dissolve about 1 g of Hyoscyamine Sulfate, accurately weighed, in 50 mL of glacial acetic acid, and titrate with 0.1 N perchloric acid VS, determining the endpoint potentiometrically. Perform a blank determination, and make any necessary correction. Each mL of 0.1 N perchloric acid is equivalent to 67.68 mg of (C17H23NO3)2·H2SO4.
Auxiliary Information—
Staff Liaison :
Elena Gonikberg, Ph.D., Scientist
Expert Committee : (MDGRE05) Monograph Development-Gastrointestinal Renal and Endocrine
USP29–NF24 Page 1095
Pharmacopeial Forum : Volume No. 31(4) Page 1078
Phone Number : 1-301-816-8251