8-Azoniabicyclo[3.2.1]octane, 3-(hydroxyphenylacetyl)oxy-8,8-dimethyl-, bromide, endo-.
3
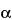
-Hydroxy-8-methyl-1
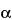 H
H,5
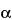 H
H-tropanium bromide mandelate



[
80-49-9].
Packaging and storage—
Preserve in tight, light-resistant containers.
Identification—
A:
Infrared Absorption  197K
197K
.
[NOTE—If differences are observed, dissolve the specimen and the Reference Standard separately in methanol, and recrystallize by adding dioxane to each solution.
]
B:
Ultraviolet Absorption  197U
197U
—
Solution:
1 mg per mL.
Medium:
alcohol.
Absorptivities at 258 nm, calculated on the dried basis, do not differ by more than 3.0%.
C:
Mercuric-potassium iodide TS produces in a solution (1 in 50) a white or slightly yellowish precipitate, but no precipitation is caused by solutions of alkali hydroxides or carbonates, even in concentrated solutions of the substance (distinction from most alkaloids).
D:
To a solution (1 in 50), add ammonium reineckate TS: a red precipitate is formed.
E:
A solution (1 in 20) responds to the tests for
Bromide  191
191
.
pH  791
791 :
:
between 4.5 and 6.5, in a solution (1 in 100).
Homatropine, atropine, and other solanaceous alkaloids—
To 1 mL of a solution of it (1 in 50), add a few drops of 6 N ammonium hydroxide, shake the solution with 5 mL of chloroform, and evaporate the separated chloroform layer on a steam bath to dryness. Warm the residue with 1.5 mL of a solution made by dissolving 500 mg of mercuric chloride in 25 mL of a mixture of 5 volumes of alcohol and 3 volumes of water: no yellow or red color develops.
Organic volatile impurities, Method I  467
467 :
:
meets the requirements.
Assay—
Dissolve about 700 mg of Homatropine Methylbromide, accurately weighed, in a mixture of 50 mL of glacial acetic acid and 10 mL of
mercuric acetate TS. Add 1 drop of
crystal violet TS, and titrate with 0.1 N perchloric acid VS to a blue-green endpoint. Perform a blank determination, and make any necessary correction. Each mL of 0.1 N perchloric acid is equivalent to 37.03 mg of C
17H
24BrNO
3.